A Deeper Dive into Second Generation Lentiviral Packaging Systems
Exploring the Advancements in Second Generation Lentiviral Packaging Systems
When it comes to gene therapy and molecular biology research, lentiviral vectors have long been a valuable tool for delivering genetic material into target cells. In recent years, second-generation lentiviral packaging systems have emerged as a significant advancement in this field, offering improved safety, efficiency, and versatility.
The Evolution of Lentiviral Packaging Systems
First-generation lentiviral vectors have limitations, including the potential for insertional mutagenesis and the risk of recombination events. Second-generation systems address these concerns by incorporating modifications such as the deletion of accessory genes and the segregation of packaging components.
One key innovation in second-generation packaging systems is the use of self-inactivating (SIN) lentiviral vectors. These vectors have a deleted U3 region in the 3′ long terminal repeat (LTR), which ensures that the viral promoter is inactive after integration into the host genome. This modification reduces the risk of insertional mutagenesis, making SIN vectors a safer option for gene therapy applications.
Enhanced Safety and Efficiency
Second-generation lentiviral packaging systems also feature improvements in safety and efficiency. The use of inducible packaging cell lines allows for tight control over viral production, reducing the risk of off-target effects. Additionally, advancements in transfection technologies have enhanced the packaging efficiency of these systems, resulting in higher viral titers and improved transduction rates.
Applications in Biomedical Research
The enhanced safety and efficiency of second-generation lentiviral packaging systems have opened up new possibilities for biomedical research. These systems are widely used in the development of gene therapies for a variety of genetic disorders, including inherited retinal diseases, immunodeficiencies, and neurodegenerative conditions.
Furthermore, the versatility of second-generation lentiviral vectors allows researchers to explore novel gene delivery strategies, such as the targeted modification of specific cell types or the delivery of therapeutic genes into hard-to-transfect cells.
Future Directions
As second-generation lentiviral packaging systems continue to evolve, researchers are actively working on optimizing vector design, improving transduction efficiency, and enhancing safety profiles. With ongoing advancements in vector engineering and gene delivery technologies, the future looks promising for the field of lentiviral-based gene therapy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, second-generation lentiviral packaging systems represent a significant leap forward in the field of gene therapy and molecular biology. These systems offer enhanced safety, efficiency, and versatility, making them valuable tools for a wide range of applications in biomedical research. As researchers continue to refine and innovate upon these systems, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in gene therapy remains high.
-
 01
01Packaging Machinery: Beyond Sealing, Driving an Efficient, Smart, and Sustainable Future
21-01-2026 -
 02
02Automatic Tray Loading and Packaging Equipment: Boost Efficiency to 160 Bags/Minute
21-11-2025 -
 03
03Automatic Soap Packaging Machine: Boost Productivity with 99% Qualification Rate
21-11-2025 -
 04
04A Deep Dive into Automatic Toast Processing and Packaging System
18-11-2025 -
 05
05The Future of Bakery Production: Automated Toast Processing and Packaging System
18-11-2025 -
 06
06Reliable Food Packaging Solutions with China Bread, Candy, and Biscuit Machines
11-10-2025 -
 07
07High-Performance Automated Food Packaging Equipment for Modern Production
11-10-2025 -
 08
08Reliable Pillow Packing Machines for Efficient Packaging Operations
11-10-2025 -
 09
09Advanced Fully Automatic Packaging Solutions for Efficient Production
11-10-2025 -
 10
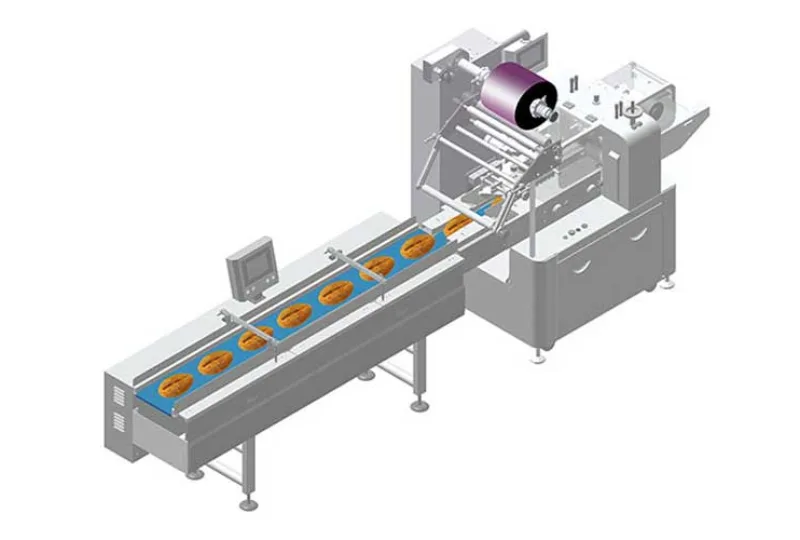
10Efficient Automatic Food Packaging Solutions for Modern Production
11-10-2025